Should Mankind Worry? The absolutely worse case scenario is mind-boggling. And it is seldom discussed beyond Academics in Graduate Studies. Only the most scholarly trained look at thee deepest possibilities in order to prepare Papers for possible Presidential Emergencies.

Will the Rarefaction3 Effect (a scientific anomaly rarely discussed) take place and force an opening in the Earth’s Atmosphere? If so, the Earth could be void of Breathable Atmosphere in as little as 72 hours or as short as 24 hours.. Only in deep caverns and saves would life survive momentarily. These Heat waves cannot be merely Observed with no regards because the worst could happen. This would be an epic cleansing on a Biblical Level. In years, Earth would be similar to Mars. But in an opposite way. Then, one day, Space Aliens might find earth.
The Rarefaction3 Effect is a hypothetical phenomenon that has not been observed or verified by scientists. It is thought to be a possible consequence of extreme heat waves, but there is no evidence to suggest that it is actually possible. But there is great debate among scholars of this extremely rare event. Could it happen?
If the Rarefaction3 Effect were to occur, it would likely cause a catastrophic loss of the Earth’s atmosphere. This would make the planet uninhabitable for humans and most other life forms.
However, it is important to note that the Rarefaction3 Effect is just a hypothesis. There is no evidence to suggest that it is actually possible, and it is therefore unlikely to occur.
The current heat waves that are being experienced around the world are certainly concerning, but they are not likely to cause the Rarefaction3 Effect. These heat waves are caused by a combination of factors, including climate change and natural variability. While they are extreme, they are not unprecedented.
It is important to stay informed about the latest climate science and to take steps to mitigate the effects of climate change. However, there should not be a need to panic about the Rarefaction3 Effect. It is a hypothetical phenomenon that has not been observed or verified.
If Earth lost its atmosphere, it would be a catastrophic event for life on Earth. The atmosphere does many things to keep us alive, including:
- Providing oxygen to breathe. The atmosphere is about 21% oxygen, which we need to breathe. Without oxygen, we would suffocate within minutes.
- Protecting us from harmful radiation. The atmosphere shields us from harmful radiation from the sun, such as ultraviolet radiation. This radiation can cause cancer and other health problems.
- Keeping the Earth’s temperature warm. The atmosphere traps heat from the sun, which helps to keep the Earth’s temperature at a comfortable level. Without the atmosphere, the Earth would be much colder.
If the Earth lost its atmosphere, all life on Earth would eventually die. Humans, animals, plants, and even bacteria would all be unable to survive without the atmosphere.
The specific effects of losing the atmosphere would depend on how quickly it happened. If the atmosphere disappeared suddenly, the effects would be immediate and catastrophic. The temperature would drop rapidly, and the Earth would be bombarded with harmful radiation. Most life on Earth would be wiped out within hours.
If the atmosphere disappeared more gradually, some life might be able to adapt. For example, some plants and animals might be able to survive in underground caves or other protected areas. However, even if some life survived, the Earth would be a very different place without an atmosphere. The climate would be much colder, and the surface of the Earth would be exposed to harsh radiation.
Losing the atmosphere is a very unlikely event, but it is something that we should be aware of. The consequences of losing the atmosphere would be devastating, and we need to do everything we can to protect our planet’s atmosphere.

If the Earth lost its atmosphere, month by month for the 1st 12 months:
Month 1:
- The temperature on Earth would drop rapidly.
- The Earth would be bombarded with harmful radiation from the sun.
- Most life on Earth would die within hours.
Month 2:
- The oceans would start to freeze.
- The Earth’s surface would become covered in dust and debris.
- Any remaining life on Earth would be struggling to survive.
Month 3:
- The oceans would be completely frozen.
- The Earth’s temperature would continue to drop.
- Any remaining life on Earth would be close to extinction.
Month 4:
- The Earth would be a frozen wasteland.
- No life would be able to survive on the surface of the Earth.
- The only remaining life would be in underground caves or other protected areas.
Month 5:
- The Earth would continue to cool.
- The atmosphere would become even thinner.
- The remaining life on Earth would be struggling to survive.
Month 6:
- The Earth would be a cold, dark, and lifeless planet.
- The atmosphere would be almost non-existent.
- Any remaining life on Earth would have died out.
Month 7:
- The Earth would continue to cool.
- The atmosphere would continue to thin.
- The Earth would be a completely lifeless planet.
Month 8:
- The Earth would be a frozen tomb.
- The atmosphere would be too thin to support life.
- The Earth would be a dead planet.
Month 9:
- The Earth would continue to cool.
- The atmosphere would continue to thin.
- The Earth would be a cold, dark, and lifeless rock.
Month 10:
- The Earth would be a frozen, lifeless rock.
- The atmosphere would be almost non-existent.
- The Earth would be a dead planet.
Month 11:
- The Earth would continue to cool.
- The atmosphere would continue to thin.
- The Earth would be a cold, dark, and lifeless rock.
Month 12:
- The Earth would be a frozen, lifeless rock.
- The atmosphere would be too thin to support life.
- The Earth would be a dead planet.
This is just a hypothetical timeline, and the exact effects of losing the atmosphere would depend on a number of factors, such as how quickly the atmosphere disappeared and how much life was able to adapt. However, it is clear that losing the atmosphere would be a catastrophic event for life on Earth.
The Earth lost its atmosphere and in 36 months later, the planet would be a very different place. The temperature would drop rapidly, and the Earth would be bombarded with harmful radiation from the sun. Most life on Earth would die within hours, and the oceans would start to freeze.
By the end of 36 months, the Earth would be a frozen wasteland. The oceans would be completely frozen, and the Earth’s temperature would be much colder than it is today. The atmosphere would be almost non-existent, and any remaining life on Earth would be struggling to survive.
The surface of the Earth would be covered in dust and debris, and the only remaining life would be in underground caves or other protected areas. The Earth would be a cold, dark, and lifeless planet.
Here are some of the specific changes that would occur to the Earth in 36 months if it lost its atmosphere:
- The temperature would drop by as much as 100 degrees Fahrenheit.
- The oceans would freeze over, and the sea level would drop by several feet.
- The atmosphere would become so thin that it would no longer be able to support life.
- The Earth would be bombarded with harmful radiation from the sun.
- Most life on Earth would die.
The loss of the Earth’s atmosphere would be a catastrophic event for life on Earth. It would make the planet uninhabitable for humans and most other life forms. The only remaining life would be in underground caves or other protected areas. But even that existence would come to an end…
It is important to note that this is just a hypothetical scenario. The Earth’s atmosphere is not going to disappear in 36 months. Only a Rarefaction3 Effect taking place would cause such an event.

However, it is important to be aware of the potential consequences of losing the atmosphere so that we can take steps to protect it.
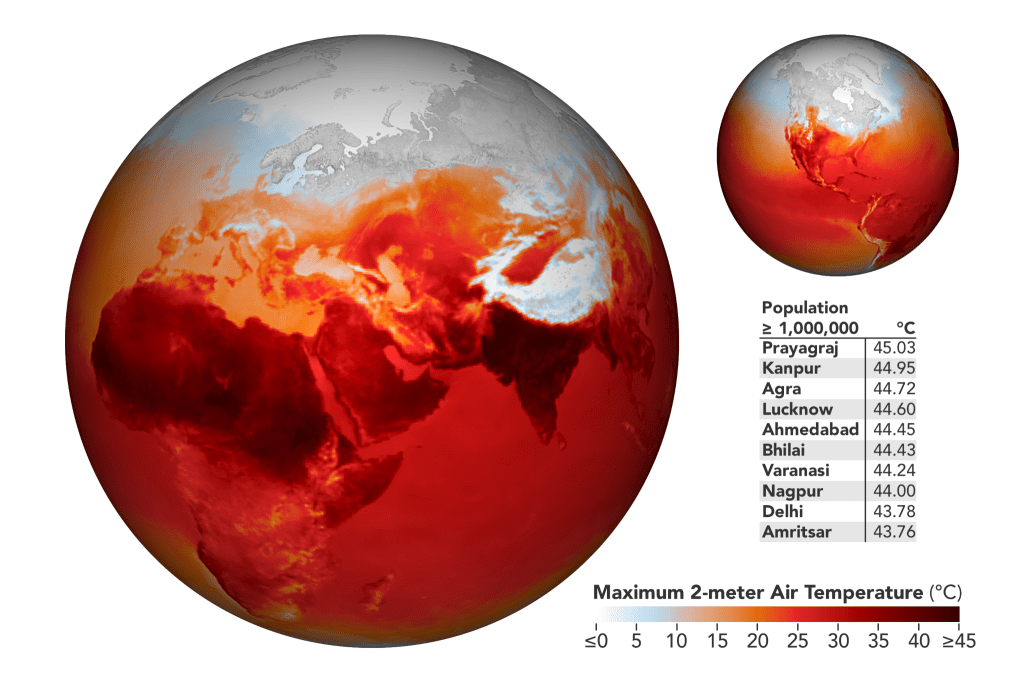
Reaching the Hottest Days on earth will ultimately have consequences. Many will die because they are not able to adapt to the extreme Heat.
It is difficult to say exactly how many deaths will be caused by the hottest days on Earth. The number of deaths will depend on a number of factors, including the severity of the heat waves, the availability of cooling infrastructure, and the health of the population.
However, it is clear that heat waves are a major public health threat. In the United States, heat waves are responsible for an average of 658 deaths per year. And, as the Earth’s climate continues to warm, heat waves are becoming more frequent and more severe.
A study by the World Health Organization (WHO) found that heat waves could cause up to 250,000 deaths per year by 2050. And, if no action is taken to mitigate climate change, the number of deaths could reach 1 million per year by 2100.
The WHO study also found that the elderly, young children, and people with chronic health conditions are the most vulnerable to heat-related deaths. These groups are less able to regulate their body temperature, and they are more likely to suffer from heat stroke and other heat-related illnesses.
In addition to deaths, heat waves can also cause other health problems, such as heat exhaustion, dehydration, and respiratory problems. Heat waves can also lead to power outages, which can further increase the risk of death and illness.
It is important to take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones from the dangers of heat waves. If you are elderly, young, or have a chronic health condition, you should be especially careful. Here are some tips for staying safe during a heat wave:
- Stay indoors as much as possible.
- If you must go outside, dress in light-colored, loose-fitting clothing.
- Drink plenty of fluids, even if you are not thirsty.
- Avoid alcohol and caffeine, which can dehydrate you.
- Take cool showers or baths.
- Use a fan or air conditioner.
- Check on elderly neighbors and relatives.
If you experience any heat-related symptoms, such as dizziness, nausea, or confusion, seek medical attention immediately.


You must be logged in to post a comment.