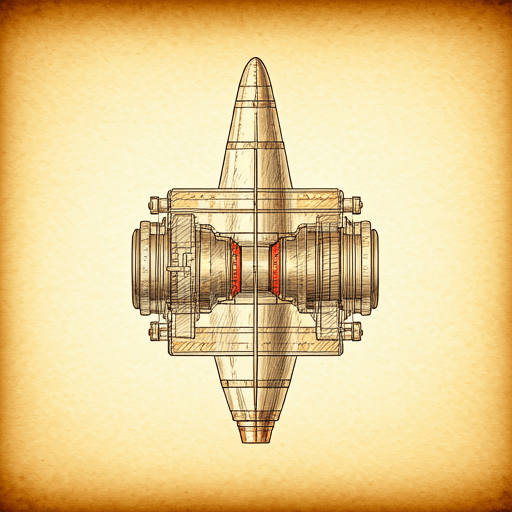
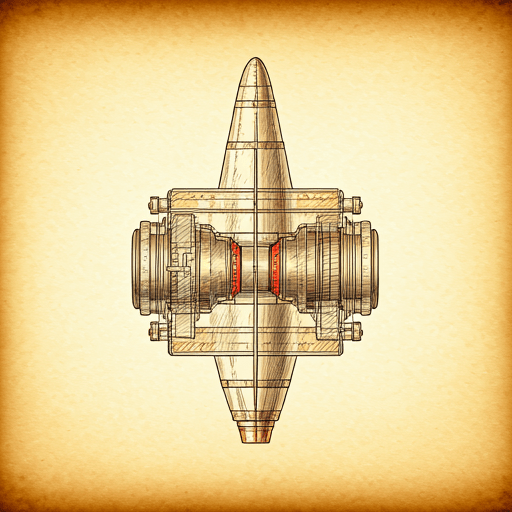
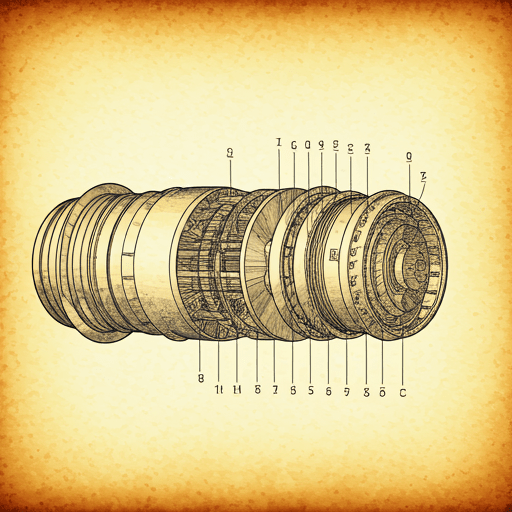
Parts of the Advanced Space Rocket Motor
Note: The specific components and their names may vary depending on the exact design and technological advancements. However, here’s a general breakdown of the major parts:
- Combustion Chamber:
- Propellant Tanks: Contain the fuel and oxidizer.
- Injectors: Introduce the fuel and oxidizer into the combustion chamber in a controlled manner.
- Igniter: Initiates the combustion process.
- Nozzle:
- Convergent Section: Accelerates the combustion gases.
- Throat: The narrowest part of the nozzle.
- Divergent Section: Further expands the gases, producing thrust.
- Turbopump:
- Turbine: Driven by hot exhaust gases to power the pumps.
- Fuel Pump: Pumps fuel into the combustion chamber.
- Oxidizer Pump: Pumps oxidizer into the combustion chamber.
- Cooling System:
- Cooling Jackets: Circulate coolant (often liquid hydrogen or oxygen) around the combustion chamber and nozzle to prevent overheating.
- Radiators: Dissipate heat from the coolant.
- Thrust Vector Control (TVC):
- Gimbaled Nozzle: Allows the engine to be tilted to control the direction of thrust.
- Vectoring Nozzles: Multiple smaller nozzles that can be individually controlled.
- Structural Components:
- Motor Case: Houses the combustion chamber, nozzle, and other components.
- Insulation: Protects the case from extreme temperatures.
- Control Electronics:
- Sensors: Monitor engine performance and conditions.
- Computer: Processes data and controls the engine’s operation.
- Actuators: Adjust valves, pumps, and other components.
- Advanced Features (Potential):
- Plasma Propulsion: Using ionized gas for propulsion.
- Nuclear Propulsion: Utilizing nuclear energy for thrust.
- Pulse Detonation Engine: Using a series of explosions for propulsion.
Image Reference: these components are commonly found in modern rocket engines.

You must be logged in to post a comment.